Based on the characteristics of pharmaceutical wastewater, physicochemical treatment is required as a pretreatment or post-treatment step in its treatment process. Currently used physicochemical treatment methods mainly include coagulation, flotation, adsorption, ammonia stripping, electrolysis, ion exchange, and membrane separation.
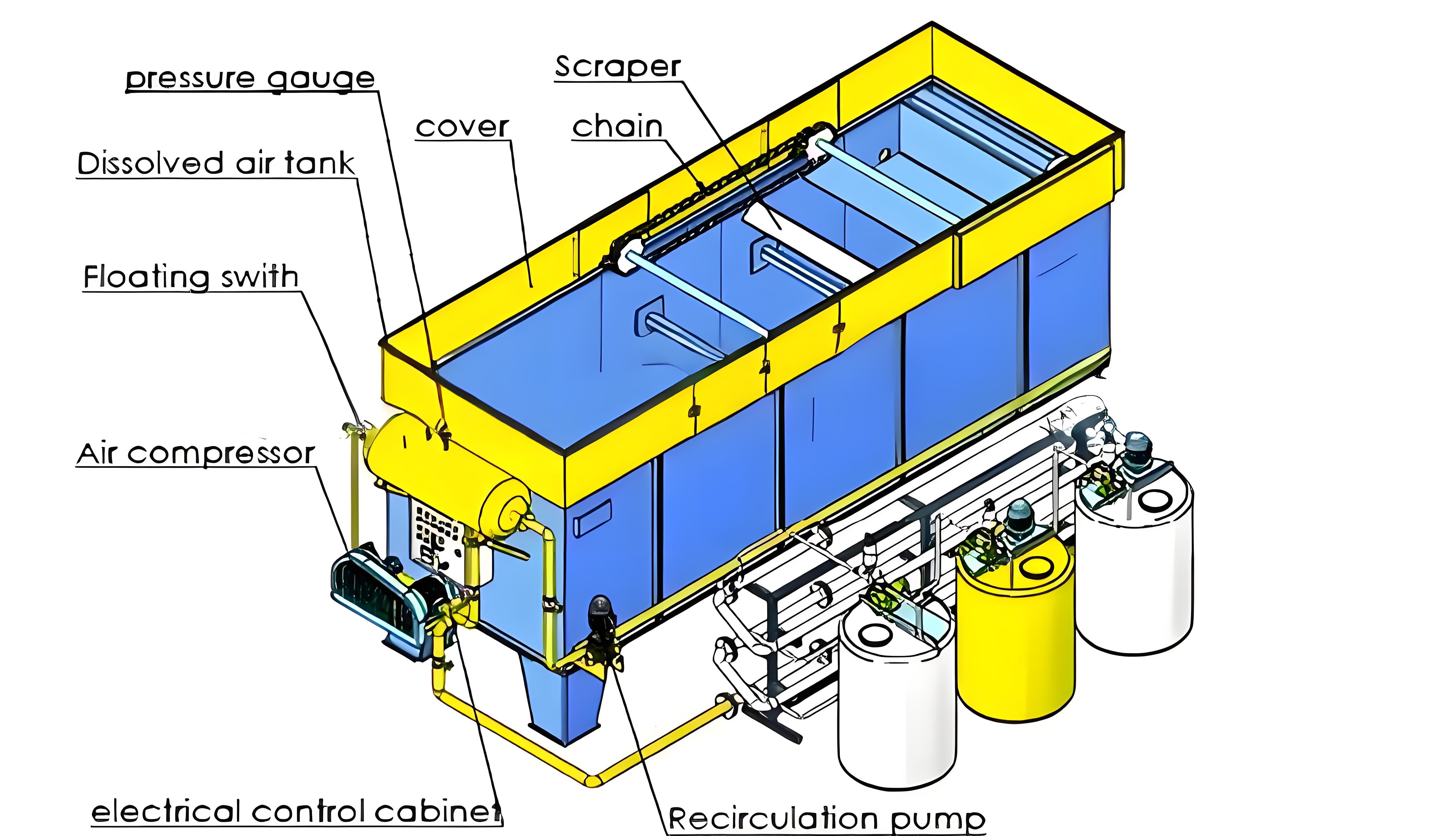
(1) Flotation Method: Flotation methods typically include various forms such as aerated flotation, dissolved air flotation, chemical flotation, and electrolytic flotation. Using a CAF vortex flotation device for pretreatment of pharmaceutical wastewater, with appropriate reagents, the average COD removal rate is around 20%.
(2) Adsorption Method: Commonly used adsorbents include activated carbon, activated coal, humic acids, and adsorption resins. A coal ash adsorption-two-stage aerobic biological treatment process was used to treat the wastewater. Results showed that adsorption pretreatment achieved a COD removal rate of 43% and improved the BOD5/COD ratio. (3) Coagulation: This technology is a widely used water treatment method both domestically and internationally. It is extensively used in the pretreatment and post-treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater, such as aluminum sulfate and polyferric sulfate for traditional Chinese medicine wastewater. The key to efficient coagulation treatment lies in the appropriate selection and addition of high-performance coagulants.
(4) Membrane Separation: Membrane technology includes reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, and fiber membranes. It can recover useful substances and reduce the total amount of organic matter discharged. The main characteristics of this technology are simple equipment, convenient operation, no phase change or chemical change, high treatment efficiency, and energy saving. A nanofiltration membrane was used to separate purulent wastewater, which showed that it reduced the inhibitory effect of purulent on microorganisms in the wastewater and also recovered purulent.
(5) Electrolysis: This method of wastewater treatment has gained attention due to its high efficiency and ease of operation. Electrolysis also has a good decolorization effect. Using electrolysis to pretreat riboflavin supernatant, the removal rates of COD, SS, and color reached 72%, 84%, and 67%, respectively.